
Jun 03, 2025
Delve into our comprehensive guide on the new EU cybersecurity legislation and learn how to prepare your organization for NIS2.
Written by Jill - Written: February 12, 2024

In the digital era, terms like cyberattacks, phishing, malware, and ransomware are more than just trendy buzzwords. They represent real threats that impact our daily lives. As our society becomes increasingly dependent on digital infrastructure, the challenge to safeguard it has never been greater. This is why Europe installed the NIS2 Directive, a powerful initiative in bolstering cybersecurity.
The new cybersecurity legislation redefines the ground rules in terms of risk management and reporting requirements, significantly expands the scope and introduces stricter penalties for non-compliance. With the October 17, 2024 deadline looming – the date by which EU countries must incorporate NIS2 into their national laws – hundreds of thousands of organizations should be gearing up for a major overhaul of their cybersecurity measures. How will this affect your company? And how should you prepare for the changes ahead?
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about the new legislation and explore its implications for your business. We’ll address the following key questions:
The NIS2 Directive (in full: Network and Information Security Directive 2022/0383) is the cornerstone of EU-wide legislation on cybersecurity. Its aim is to enhance the security of network and information systems in Europe. It mandates that operators of critical infrastructure and providers of essential services implement necessary security measures and report incidents to the authorities.
NIS2 is an update to the original NIS1 Directive from 2016, and it came into effect in January 2023. EU member states have until October 17, 2024, to transpose the directive into national legislation. This means that every organization falling within its scope will be legally required to comply with its requirements by the end of 2024. Overall, NIS2 involves more than 160,000 organizations across Europe.
In recent years, the security of our society has been increasingly challenged by developments such as COVID-19, the war in Ukraine, and emerging cyber threats. Concurrently, our reliance on network and information systems has grown, necessitating an update to the existing legislation to enhance the digital and economic resilience of EU member states.
Compared to NIS1, the scope of the legislation has been significantly expanded. Also, the mandatory security measures and incident reporting have been tightened, and consequences for non compliance are much stricter.
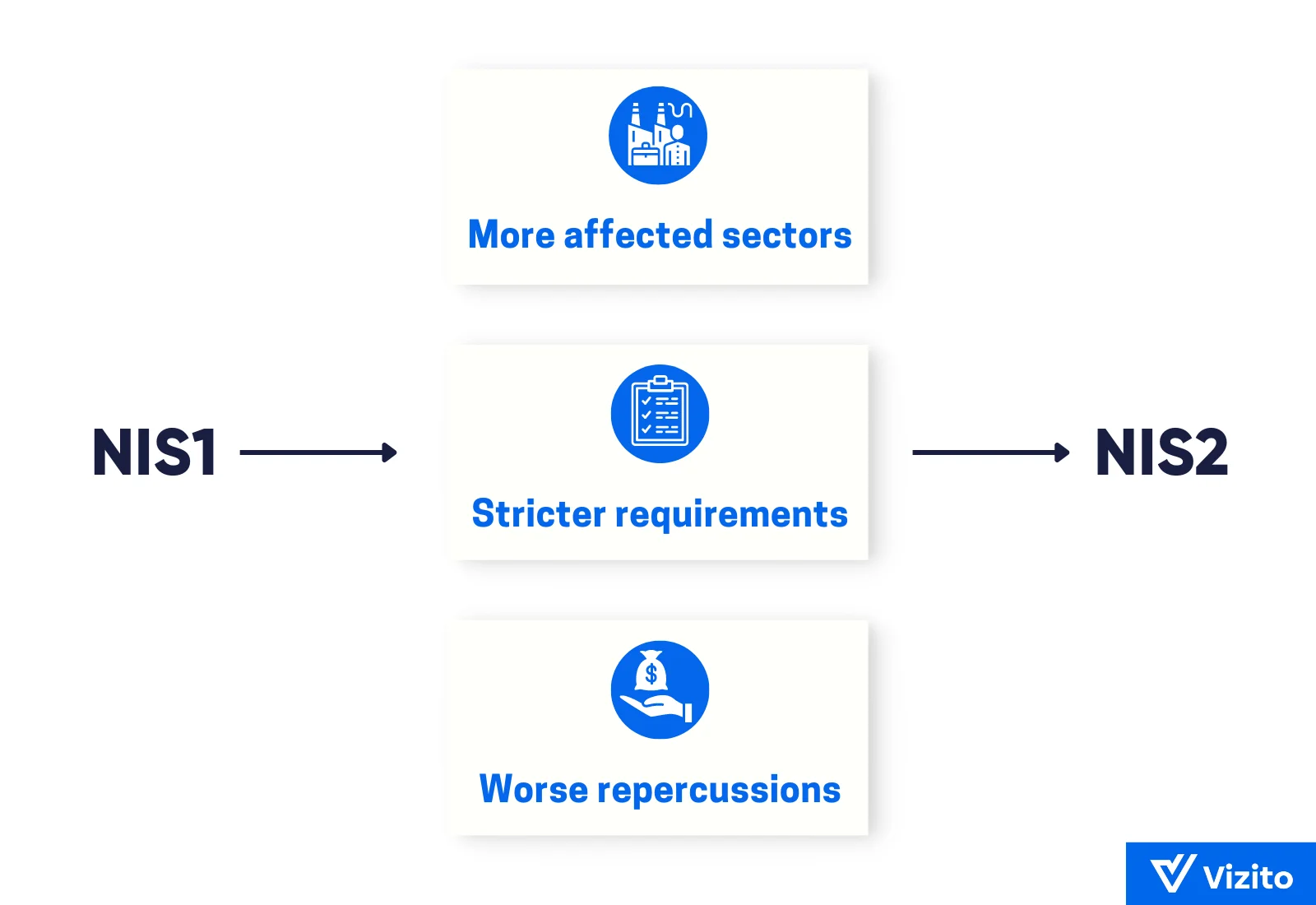
Does your organization fall under the scope of the NIS2 Directive? This is where things get a bit more complicated, but bear with us as we guide you through the matter step by step.
First, let’s look at the 18 sectors to which NIS2 applies. The directive divides these into two categories: ‘highly critical’ and ‘other critical’. The distinction lies mainly in the supervision measures and penalties; we’ll get back to this later. Organizations in both categories, however, must meet the same requirements.

If your organization falls under one of these categories, you may be impacted by NIS2.
Are you still with us? To complicate things a bit further, NIS2 defines two categories of organisations that must comply with the legislation: ‘essential’ and ‘important’ entities.
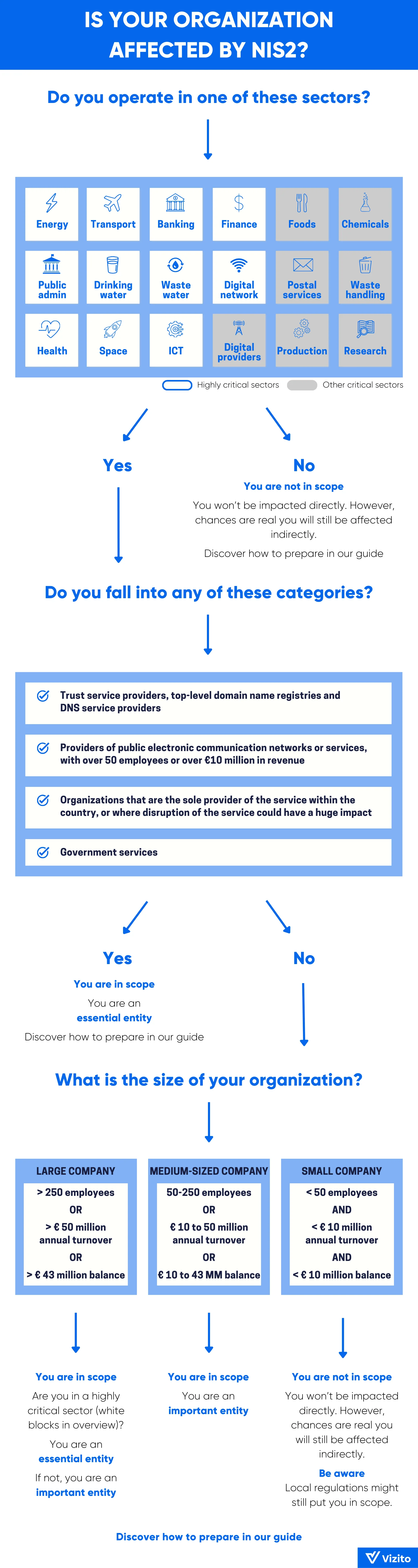
Small enterprises with less than 50 employees and a turnover of less than 10 million euros are not automatically excluded. Member states may consider them as ‘critical’ or ‘important’ if their services play a key role in society or if disruption of their services would have significant consequences for public health or safety.
Essential entities may be proactively checked for compliance with NIS2, while important entities are only investigated following a complaint.
If your organization is not based in the EU, you might think that NIS2 doesn’t apply to you. Unfortunately, if your organization falls under any of the previously mentioned categories and provides services within the EU, you are required to comply with the NIS2 Directive.
The NIS2 Directive lays out specific guidelines for non-EU organizations. Non-EU entities providing services within the EU are required to designate a representative in a EU member state where the services are provided. This person will have to oversee the organization’s compliance with NIS2.
If your organization isn’t part of the scope, you won’t have to worry about fines or immediately adhering to the regulations. However, chances are real you will still be impacted by NIS2.
For example, if you provide services or products to an entity that is within the NIS2 scope, that client may require you to meet a certain level of cybersecurity. In this case, you won’t be audited by authorities overseeing NIS2 compliance, but by your client instead.
It might be wise to consider aligning your security measures with the NIS2 Directive anyway. This approach makes it easier to collaborate with other companies, and you can assure your clients that you are compliant and trustworthy.
So, your organization falls within the scope of the NIS2 Directive. What does this mean for you, and what are the next steps?
By April 17, 2025, member states must identify all essential and important entities that fall within the scope. Details about the registration process will become clear once the directive is transposed into national law. At the very least, the registration will include the following information:
This brings us to the main question: what are the measures and obligations for organizations within the scope? NIS2 divides the requirements into four main domains:
Besides these four main areas, NIS2 provides 10 basic security measures for essential and important entities:
Let’s hope you won’t need this section, but if a security incident occurs, you’ll need to notify the appropriate authorities. These are the new guidelines:
As we discussed earlier, the NIS2 Directive defines two categories for organizations within its scope. Don’t worry if you’re finding it hard to see the forest for the trees: here’s a brief recap.
Requirements for both categories are the same; the distinction lies in the supervision measures and sanctions, as the tables below demonstrates.
| Essential entities | Important entities |
|---|---|
| Fines: €10 million or 2% of global annual revenue |
Fines: €7 million or 1,4% of global annual revenue |
| Non-monetary penalties: - Compliance orders - Binding instructions - Security audit implementation orders - Threat notification orders to entities’ customers - Criminal sanctions for management |
Non-monetary penalties: - Compliance orders - Binding instructions - Security audit implementation orders - Threat notification orders to entities’ customers - Criminal sanctions for management |
! Member states may provide that fines do not apply to government bodies. However, the other penalties will apply.
| Essential entities | Important entities |
|---|---|
| Active controls: external audits, inspections, documentation requests |
Ex-post supervision: action is taken when authorities receive evidence of non-compliance |
What’s next for your organization?
If you’re not part of the scope, you can breathe easily. But you’re not completely off the hook. Make a list of companies you work with that will need to comply with NIS2 and consider what this means for your organization. And think about whether and how you can apply the new security measures anyway, as they will bring you benefits in the end.
If you are within the scope, it’s time to get to work. We recommend following these steps to get started with NIS2 preparations:
1. Do a risk assessment. Which are potential security risks? How likely are they to happen? What is the potential impact? And which measures are already in place to limit risks?
2. Update your security policies. Based on the risk assessment, update existing security policies or develop new ones. Make sure you cover the 10 basic requirements of NIS2.
3. Implement security measures. Options include: enhanced network security, stricter access controls, encryption, and securing the supply chain. A digital visitor management system can significantly help you: it gives control over your visitor management, stores visitors’ personal data securely, and simplifies incident reporting by maintaining accurate records of all visitor activities.
4. Develop procedures for detecting, monitoring, resolving, and reporting incidents.
5. Train Management and Staff. Which staff members perform critical functions within the organization? Make them aware of the risks and safety measures.
6. Prepare for audits and inspections. Maintain clear and comprehensive records of your security policies, risk assessments, incident reports, and compliance activities.
The NIS2 Directive represents a milestone in the European Union’s policy to strengthen cybersecurity standards within its borders. For organizations falling under this regulation, complying with NIS2 is not just a legal obligation, but also an opportunity to enhance their cybersecurity, protect their data, and build trust with customers and partners.
The directive demands a proactive approach, and the adoption of a digital visitor management system plays a key role in this context. Such a system aids in complying with NIS2 standards in several ways. It enhances access control and protects visitors’ personal data from cyber threats. Additionally, the system maintains accurate logs of visitor activities, which simplifies the assessment of potential risks, strengthens the security of the supply chain, and facilitates incident management and reporting in the event of a security incident.
To get a feel of how a modern visitor management system can help your business, try out Vizito during a 14-day trial. Chat with us or book a demo to discuss how Vizito can help you improve your reception.